-
The war of copper vs fiber has raged for years. Fiber seems to operate as a rival to copper rather than a replacement until now, it has already established a niche in the industry. However, with recent advances in copper technology, the copper presents the same step-ladder upgrade path. The speed difference between the two media is considerably smaller. In some ways, the copper matters most to IT experts and data center decision makers. But many end-user organizations still face tough decision about which type is the best overall value for their current and future projected needs. This battle is also being waged in SFP transceivers, there is a measurable difference in the copper SFP vs optical SFP. This article will explore their respective strengths and weaknesses and reveal insights into how IT experts are to proceed.

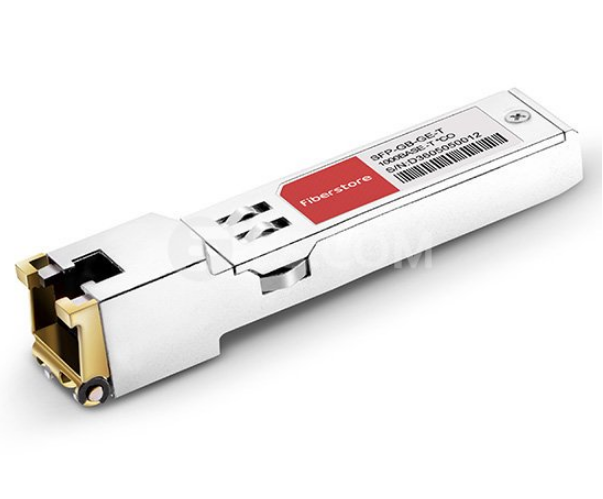
Copper SFP vs Optical SFP: Copper SFP Is a Balanced Choice in Environment Restrictions
The Gigabit RJ45 copper SFP transceiver supports 1000Mbps over Cat5 cables with RJ45 connector interface, which operates on standard Cat5 unshielded twisted-pair copper cabling of link lengths up to 100 m (328 ft). GLC-T is a typical Cisco 1000BASE-T SFP copper RJ-45 transceiver. For short-distance links on a Gigabit switch, it makes no difference if you use SFP ports or RJ45 ports to interconnect switches. Copper SFP is popular to be used for short range uplinks, as it’s easier and cheaper to use 1G copper SFPs and patch cables. And SFP ports are primarily for allowing fiber connections over longer distances. Especially in some case, Copper SFP will make sense if the switch on one side does not have copper ports but SFP slots and the switch on the other side only has copper and can’t be fitted with fiber ports. Or if you don’t need the distance of fiber, you can consider converting SFP to RJ45, which will depend on the switch to determine what copper speeds (10/100/1000) are supported on a copper SFP. Moreover, using copper SFPs to connect the regular copper Gigabit ports is a wise choice to make the best use of the corresponding number of SFPs on existing connected switches.

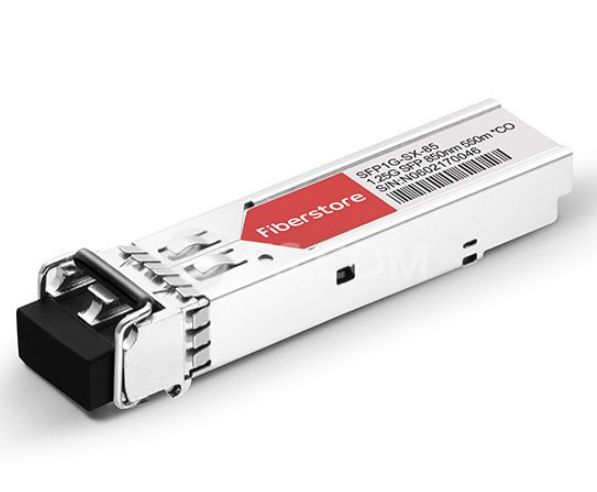
Copper SFP vs Optical SFP: Fiber SFP Is More Flexible in Long Distance
The optical fiber SFP modules with LC or SC optical connectors are available in Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. And these SFP modules are industrially rated to perform in the most difficult operating environments. The SFP fiber module offers different wavelengths and optical power budget to allow distances from 550m to 120km. A variety of 1Gbps SFP modules in different distance can be found in FS.COM. Some statics also shows that the legacy SFP can hit 4.25Gb/s at 150m, or up to 1.25Gb/s for 160km runs and a variety of ranges/speeds in between depending on type of fibre. Generally, when the distance of the run is over 328 ft/100 m, fiber SFP module must be considered instead of copper SFP RJ45 module, since 1000Mbps could only go as far as 100m over copper cabling. In that sense, optical fiber SFP offers the substantial advantage over copper SFP.

Copper SFP vs Optical SFP
- Operating Temperature
For the standard fiber SFP and copper SFP, there is no difference for the operating temperature - they support 0 to 70°C (32 to 158°F) case temperature as default. In fact, there is more heat dissipated for optical or electrical transmission in the specific applications. Generally, the copper SFPs run much hotter than the fiber SFPs. There are two factors that affect the temperature: power consumption and the case surface. The typical power consumption of fiber SFPs is 0.8W, the copper SFP is 1.05w, that's why copper SFP have a higher case temperature. In the same environment, the fiber SFP runs at 40°C (104°F) while the copper SFP should run around 52°C (126°F).
- Distance
As mentioned above, copper SFP supports the max cable distance is 100m, so it is commonly used to interconnect between switches and servers in horizontal and shorter-length backbone applications. While the fiber SFP allows the transmission distance up to 120km, which demonstrate the high performance over longer distances.
- Security
When security could be considered as a problem in the connection, using fiber SFP module is better than RJ45 copper SFP module. Because fiber doesn’t conduct electricity that makes it resistant to lightning strikes.
- Cost
Copper SFP transceiver might be more expensive than fiber SFP module in the same short distance. In Gigabit Ethernet applications, when copper SFP is used in combination with cooper cables in short runs, it is more cost effective as the copper cables are more cheaper than fiber cables. Besides, with the boom of third-party vendors, their full-compatible and trustworthy fiber SFP modules are developed to support lower cost fiber runs. The price gap between 100m copper transceiver and 40km 1000BASE-EX SFP fiber transceiver is reduced. More choices are provided for customers to meet their specific demands.
FS P/N Description FS.COM Price SFP-GB-GE-T Cisco GLC-T Compatible 1000BASE-T SFP Copper RJ-45 100m Transceiver $ 21.00 SFP1G-SX-85 Generic Compatible 1000BASE-SX SFP?850nm 550m DOM Transceiver $ 6.00 SFP1G-EX-55 Cisco GLC-EX-SM1550-40 Compatible 1000BASE-EX SFP?1550nm 40km DOM Transceiver $ 24.00 Conclusion
Through copper SFP vs optical SFP, we can see that each technology has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Optical fibre SFP is not necessarily better than copper SFP. In fact, mixing copper and fiber solutions is the best practice for data center, as a versatile solution is critical to ensuring the data center remains both manageable and scalable when performance demands skyrocket. Network industry is unpredictable, and the demands of tomorrow may require facilities to investigate solutions they may have scoffed at a year ago.
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire
-
In the early stage of optical fiber communication, one optical fiber can only transmit signals of one wavelength. This is known as conventional two-fiber Bi-Directional communication - at least two fibers are needed to accomplish the full-duplex communication with TX and RX optical signals. With the development of WDM technology, transmitting and receiving of optical signals on separate wavelength can be achieved through only one single fiber. This single fiber BiDi transmission gradually becomes a popular and cost-effective solution for today’s data center and IT infrastructure, because it helps to maximize the capacity and usage of optical fibers. Consequently, BiDi optical transceiver as the basic component plays an irreplaceable role in the WDM BiDi transmission application. This article will generally introduce Cisco BiDi SFP transceivers, including GLC-BX-U, GLC-BX-D, GLC-BX-20U, GLC-BX-20D, GLC-BX40-D-I, GLC-BX40-U-I, GLC-BX80-D-I, GLC-BX80-U-I, GLC-BX120-U, GLC-BX120-D, etc.
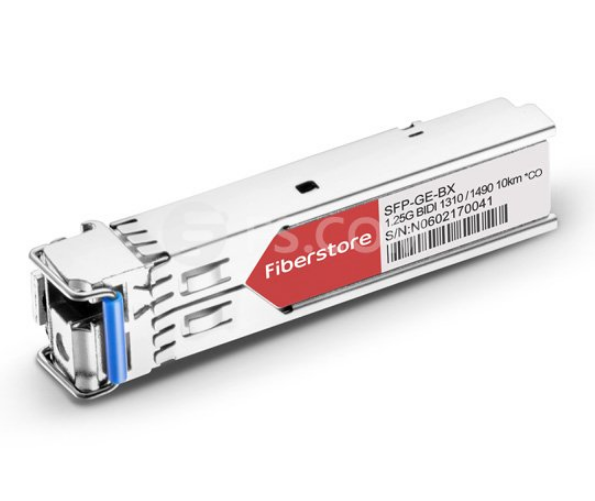

What Is a BiDi SFP?
BiDi SFP transceiver can be defined as a compact, hot swappable, input/output optical module that can transmit and receive data to/from interconnected equipment through a single optical fiber. Unlike traditional optical transceivers, BiDi optical transceivers are fitted with wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) diplexers, which combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. To simplify it, conventional optical module has two ports - the TX for the transmit port and the RX for receive port; but BiDi transceiver has only one port to complete the 1310nm optical signal transmitting and 1550nm optical signal receiving, or vice versa. Therefore, BiDi transceivers must be deployed in matched pairs with their diplexers tuned to match the expected wavelength of the transmitter and receiver. These BiDi optical transceivers can offer bi-directional data links over single-mode fiber up to 120 km. BiDi SFP transceiver is applicable to many access networks: passive optical networks (PON) and point-to-point, digital video and closed circuit television (CCTV) applications, inter-system communication between servers, switches, routers, optical add drop multiplexer (OADM), WDM fast Ethernet links, SDH/STM-1, SONET/OC3, metropolitan area networks and other optic link.
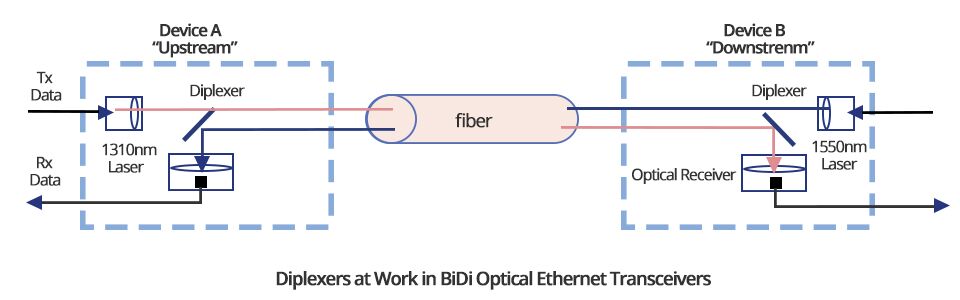
Common Types of Cisco BiDi SFP
1G BiDi SFP is also known as 1000BASE-BX SFP, which use two different wavelengths (1310nm-TX/1490nm-RX, 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX, 1490nm-TX/1550nm-RX and 1510nm-TX/1570nm-RX) for transmission in different distance. The following will list some main Cisco BiDi SFP modules in 10km, 20km, 40km, 80km and 120km.
10km Cisco BiDi SFP
The Cisco GLC-BX-D and GLC-BX-U is a pair of 10km BiDi SFP transceiver with LC duplex connectors, operating on a single strand of standard SMF. The GLC-BX-U transceiver operates at 1310nm-TX/1490nm-RX wavelength with upstream bidirectional single fiber, while the GLC-BX-D transceiver operates at 1490nm-TX/1310nm-RX wavelength with downstream bidirectional single fiber. These two BiDi optical modules, compliant to 1000Base-BX standard, are rated for distances up to 10 km over SMF and a maximum bandwidth of 1Gbps. A 1000BASE-BX-D device is always connected to a 1000BASE-BX-U device with a single strand of standard SMF. In addition, the GLC-BX-D and GLC-BX-U BiDi SFPs also support digital optical monitoring (DOM) functions according to the industry-standard SFF-8472 multisource agreement (MSA). This feature gives the end user the ability to monitor real-time parameters of the SFP, such as optical output power, optical input power, temperature and transceiver supply voltage.
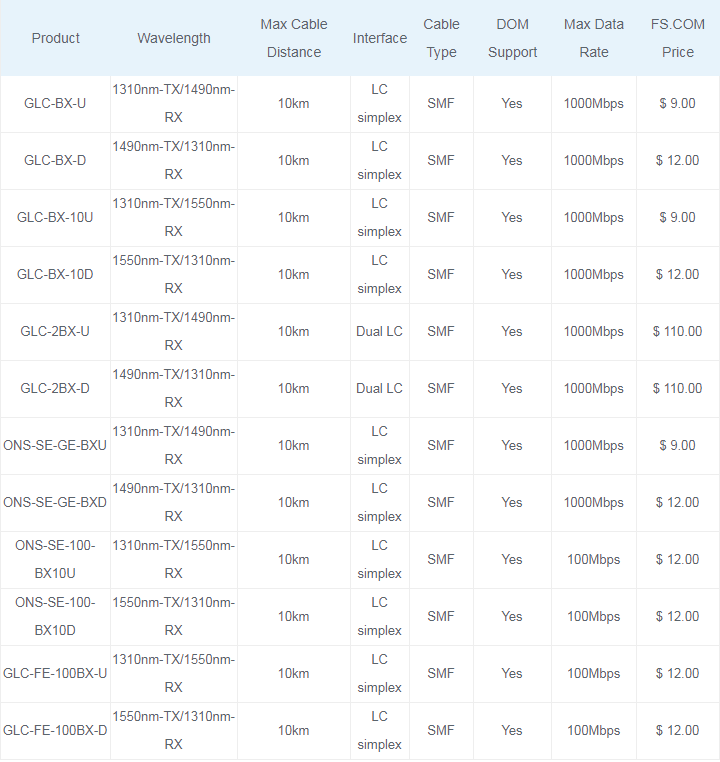
(GLC-2BX-U and GLC-2BX-D are 2-channel 1000BASE-BX SFP modules, also known as compact SFPs that integrate two IEEE 802.3ah 1000BASE-BX10 interfaces in one SFP module. They are designed to connect to any standard-based Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) in FTTx links.)
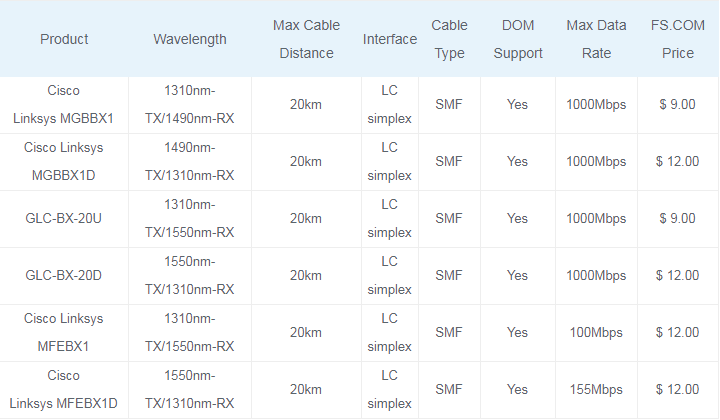
20km Cisco BiDi SFP
GLC-BX-20U and GLC-BX-20D are Cisco 20km BiDi SFP transceivers that work with single mode fiber. The GLC-BX-20U operates at 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX wavelength, and GLC-BX-20D operates at 1550nm-TX/1310nm-RX. So these two BiDi SFPs always work in pairs. Their max data rate is 1000Mbps. FS.COM compatible Cisco BiDi transceivers are high performance, cost effective modules supporting data-rate of 1000Mbps and 20km transmission distance with SMF. Among the Cisco 20km BiDi SFPs, Cisco Linksys MFEBX1D provides up to 155Mbps bi-directional data transfer rate at distances up to 20km on a single fiber core. These bidirectional SFP transceivers allow data transfer in either direction through a single optical fiber by employing separate wavelengths travelling in either direction.
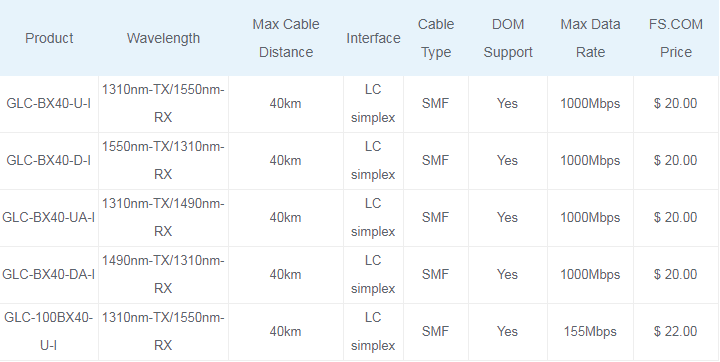
40km Cisco BiDi SFP
Cisco GLC-BX40-D-I and GLC-BX40-U-I is a pair of 40km BiDi SFP modules for Gigabit Ethernet 1000BASE-BX and Fiber Channel communications. They support link length of up to 40km point to point on single mode fiber at 1Gbps bidirectional and use an LC connector. The GLC-BX40-D-I is 1550nm-TX/1310nm-RX 40km BiDi WDM SFP simplex transceiver module, GLC-BX40-U-I is 1310nm-TX/1550nm-RX BiDi WDM SFP module. They are specified for duplex optical data communications such as 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet per IEEE802.3z and 1G Fiber Channel extended reach application.
80km Cisco BiDi SFP
The Cisco GLC-BX80-D-I and GLC-BX80-U-I SFPs are 1G BiDi SFP modules that provide 80km transmission distance over single strand of single-mode fiber. GLC-BX80-D-I operates at 1570nm-TX/1490nm-RX wavelength, whereas GLC-BX80-U-I operates at 1490nm-TX/1570nm-RX. These bidirectional SFP transceivers are intended mainly for connecting high-speed hubs, Ethernet switches, and routers together in different wiring closets or buildings using long cabling runs, and developed to support longer-length on fiber backbones. Compared with commonly used dual fiber SFP transceiver modules, the BiDi SFP transceiver allows end users to reduce the total cost on fiber cabling infrastructure by requiring half of fiber cables, providing increased transmission capacity very convenient without installing new fibers.
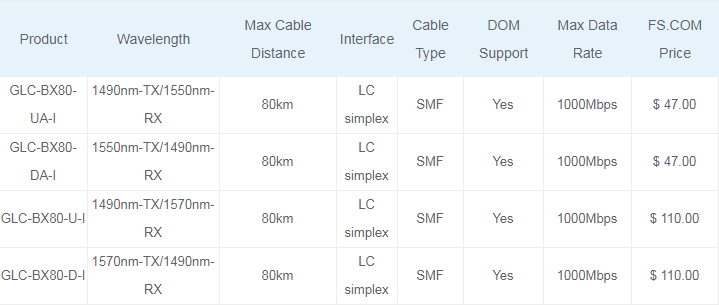
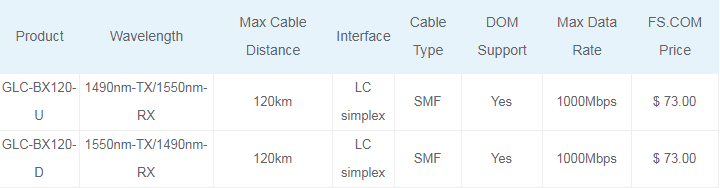
120km Cisco BiDi SFP
The Cisco GLC-BX120-U and GLC-BX120-D are 1490nm and 1550nm bidirectional SFP transceivers that are used with single mode optical fiber. They also use two wavelength 1490nm-TX/1550nm-RX(1550nm-TX/1490nm-RX) simultaneously. These BiDi SFP modules can support transmission distance up to 120 km, which are connected through pluggable LC connector type optical interface. They have a DFB (Distributed Feedback) type transmitter, an APD (Avalanche Photo-Diode) type receiver, an LD (Laser Driver), a limiting amplifier and digital diagnostic monitor. Those BiDi SFP transceivers are Class 1 laser safety product which complies with US FDA regulations, SFP MSA, SFF-8472 and RoHS standards. More importantly, 120km SFP modules have the same or even lower transmit power as compared to 80km SFP. It is the reason that 120km modules extend the range thanks to receiver not transmitter. 120km modules have much better receiving sensitivity than 80km modules.
Conclusion
BiDi SFP transceiver serves as an ideal and feasible solution in situations where only limited fibers or limited conduit space is available. And the deployment of BiDi optical transceivers efficiently enhances the bandwidth capacity of the existing optical fiber infrastructure and help to achieve economical and reliable performance of the optical network. Although BiDi transceivers may be more expensive than common transceiver modules, they can save you the cost on fiber cables from the long run.
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire
-
1000BASE-X is a group of standards for Ethernet physical layer standards, which is used for gigabit Ethernet connections that transmit data mainly over fiber optic cable or copper-shielded cable. There are several 1000BASE-X interface types used in SFP transceiver modules, including 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX and 1000BASE-EX. Besides, SFP transceivers are available with different transmitter and receiver types, allowing users to select the appropriate transceiver for each link to provide the required optical reach over the available optical fiber type (eg: multimode fiber or single-mode fiber). 1000BASE-LX SFP and 1000BASE-SX SFP are two common types of optical transceiver modules in the market. Today’s topic will discuss 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode vs. 1000BASE-LX SFP single-mode.

1000BASE-SX SFP VS. 1000BASE-LX SFP
1000BASE-SX SFP Transceivers for Multimode Fiber Only
1000BASE-SX is a physical layer specification for Gigabit Ethernet over fiber optic cabling as defined in IEEE 802.3z. The SX systems operate full-duplex with multimode fiber only, using the cheaper 850nm wavelength laser diodes. The maximum distance supported varies between 220 and 550 meters depending on the bandwidth and attenuation of the fiber optic cable used. The standard 1000Base-SX NICs available today are full-duplex and incorporate LC fiber connectors. So 1000BASE-SX SFP supports link length of up to 550m (depending on fiber type) on multimode fiber at 1Gbps. This optic works at 850nm wavelength and uses a LC connector. Take Cisco GLC-SX-MM for example, this 1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver is able to realize 550m link length through OM2 MMF with LC duplex.
1000BASE-LX SFP Transceivers for Both Multimode and Single-Mode Fibers
As opposed to 1000Base-SX, 1000BASE-LX uses long wavelength laser over both multimode and single-mode fiber. It has a working distance of up to 10 km over single-mode optic fiber, and a maximum length of 550 meters on multimode fiber. So the 1000BASE-LX SFP can operate on standard single-mode fiber optic link spans of up to 10 km, and up to 550 m on any multimode fibers. Arista Networks SFP-1G-LX is 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver that operates over a wavelength of 1310nm for 10 km on SMF and 550m on MMF.
Single-mode SFP VS. Multimode SFP
SFP modules can be divided into single-mode SFP and multimode SFP modules. For single-mode SFP modules, there are “LX” for 1310nm and “EX” “EZX” for 1550nm. Single-mode fiber SFP is designed to transmit signals over long distances. So the single-mode module works mainly in the 1310nm and 1550nm wavelengths and is mostly used in a long distances transmission environment reaching 2 km, 10 km, 40 km, 60 km, 80 km and 120 km. For example, Cisco GLC-ZX-SM is a single-mode module, which operates over a wavelength of 1550nm for 80 km.
Single-mode SFP(extraction lever):
- LX - 1310 up to 10km
- EX - 1310 up to 40km
- ZX - 1550 up to 80 km using green ex lever
- EZX - 1550 up to 160 km

NOTE:
- Black color coded bale clasp designates a Multi-mode SFP
- Blue color coded bale clasp designates the 1310nm SFP
Comparatively, multimode SFP transceivers are identified with “SX”. This MMF SFP optics is specially for short distance data transmission. The common multimode SFP modules work in 850nm wavelength and is only used for short distance transmission reaching 100m and 500m. Though it’s not able to transport for long distance, it can transport many kinds of optical signals. For instance, Cisco GLC-SX-MMD is a typical multimode fiber transceiver, which operates over a wavelength of 850nm for 550m.
1000BASE-SX SFP Multimode VS. 1000BASE-LX SFP Single-mode
- Standard
SX stands for short wavelength. The standard specifies a distance capability between 220 meters and 550 meters. The “LX” in 1000BASE-LX stands for long wavelength, indicating that this version of Gigabit Ethernet is intended for use with long-wavelength transmissions (1270 - 1355nm) over long cable runs of fiber optic cabling. 1000BASE-LX can run over both single mode fiber and multimode fiber with a distance of up to 10 km and 550 m, respectively.
- Types of Optical Fibers
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP module will work with single-mode fiber in order to perform both transmission and reception of data. Whereas 1000BASE-SX multimode SFP transceiver will work with multimode fiber, which has a thicker core and allows higher speed at shorter distance.
- Transmission Distance
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP transceivers are mostly used in long distances (up to 10 km) transmission environment. 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode is only used for short distances (up to 550m), like in small area or within the building.
- Wavelength
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP works in 1310nm, whereas 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode works in 850nm.
- Transmission Medium
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP transport the optical signal for long distance, but there is only one signal in the “tunel”. 1000BASE-SX multimode SFP has many optical signal in one “tunel”, the signals may affect each other. So it can transport many kind of optical signals.
- Dispersion
1000BASE-SX multimode optics are affected by modal dispersion, because the light rays follow different paths through the fiber and arrive at different times on the other end. This is the main reason the distance on this type of optic is limited. Whereas 1000BASE-LX single-mode optics are affected by wave guide dispersion, caused by the light going down the fiber being wider than the core of the fiber. This allows more control of the path of the photons, but is more affected by micro bends, twists and stress on the fiber.

Conclusion
Through 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode vs. 1000BASE-LX SFP single-mode, we could actually conclude that the 1000BASE-SX standard was developed to support lower cost multimode fiber running in horizontal and shorter-length backbone applications, while the 1000BASE-LX standard was developed to support longer-length multimode building fiber backbones and single mode campus backbones. With so many types of SFP modules available in the market, careful notice should be given to the range of differences, including transmission distance, wavelength, cable types, price, etc.
Related Article: The Basics of 1000BASE-SX and 1000BASE-LX SFP
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire
-
Due to the increased requirements for IP surveillance networks, the appearance of PoE switches give you an easy way to add PoE devices to the network. They are ideal for small business networks that need to inexpensively use PoE to deploy wireless access points, VoIP phones and IP cameras. The PoE switch models are available with 4, 8, 16, 24 or 48 ports, although other variants are also available. 24 port PoE switch is the most prevalent variant on the market. So why your network needs a 24-port PoE switch and how can network benefit from deploying it? This article explains it in detail.

Why Your Network Needs A 24-Port PoE Switch?
When choosing an Ethernet switch, the most important is to check whether the numbers of ports on the switch are enough to connect all your devices. The same is true when choosing PoE switch. PoE ports are flexible to connect with Cat5e cable without additional settings. Generally, the PoE switch has the uplink ports, which allow long distance data transmission between switches. Switches without uplink ports can still be linked together but you may experience bandwidth issues with switch to switch data flow. A 24-port PoE switch fully complies to the the IEEE 802.3af standard for PoE up to 15.4W per port and the latest IEEE 802.3at standard for PoE+ up to 30W per port. On the whole, the 24-port PoE switch can greatly reduce the associated cost with smaller PoE installations in a home or small business environment. At the same time, it will allow you to expand your network to areas with no power lines. Essentially, the plug-and-play PoE switch will automatically detect whether connected devices are PoE and send power accordingly. For a 24-Port Gigabit PoE managed switch with a power budget of 360W, you need a total power per port of 30W to power an IP camera network. And you can continue to add IP cameras until you reach your budget. If you have 2 SFP ports, you can also connect to multiple switches. Keep in mind, if you exceed the power threshold and the devices aren’t getting sufficient power, they may not boot up properly. Finally, please ensure you check the power requirement for your PoE enabled device, the standard it complies to and the overall PoE budget of your installation before purchasing a 24-Port PoE switch.

FS S1400-24T4F 24-Port Gigabit PoE Managed Switch - 4 SFP, 400W
FS S1400-24T4F managed PoE switch comes with 24 10/100/1000Base-T RJ45 Ethernet ports, 1 console port, 2 combo port and 2 dedicated SFP ports for fiber uplinks. It offers network managers the advantage of connecting up to 24 power-hungry wireless access points, IP security cameras, LED lighting or VoIP endpoints to the network with a single wire for power and connectivity. With its robust PoE power budget of 400W, the S1400-24T4F switch supports denser deployment of PoE devices. This switch has 52Gbps switching capacity with 8K MAC address table, 9KB Jumbo Frame and 4MB Buffer Memory. Power supply is supportive as well, which is about 100-240V. This is a solidly built excellent switch from the firm with a data transfer rate of 1,000 Mb/s. What’s more, it offers configurable Layer 2+ network switching features like VLANs and fast Ring Protection Protocol(RSTP), which achieved real ring loop redundancy protection. It represents an ideal switching solution for even advanced SMBs or entry-level enterprise which demands industrial, surveillance, IP Phone, IP Camera or Wireless applications. All in all, the PoE switch provides security, performance, quality of services, central managed and other network control capabilities.
 Features:
Features:- 400W PoE budget available across 24 Gigabit PoE ports
- 4 Gigabit SFP fiber ports for aggregation to the network core
- Support various advanced management, such as WEB, CLI, TELNET, SNMP
- Support Port-based VLAN, IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and GVRP, simplify the network planning
- Support PoE intelligent management system, timing of PoE power supply, power online configuration, voltage and current online monitoring etc.
- Switching capacity with 52Gbps line rate fabric for maximum throughput across all 24 ports of Gigabit Ethernet
Conclusion
PoE switch is a cost-effective solution to increase the reliability and security of networks by providing centralized backup power to all connected IP surveillance devices. Before purchasing PoE switches, try to know as more details about the switch specifications as possible and also your own needs. FS S1400-24T4F managed PoE switch is an affordable switch to support SMB switching needs for wireless converged networks and IP surveillance. If you prepare for growth and buy infrastructure for the long-term, you will find this 400W PoE power budget provides headroom for future expansion.
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire
-
Optical transceivers play a key role in handling all storage, data, voice and video traffic whether linking rack to rack, bottom to top of rack, data center to data center or enterprise networks to network. A range of flexible fiber optic transceiver modules cover all of network needs, such as SFP, SFP+, QSFP, QSFP28, CFP, etc. But for 10G DWDM tunable SFP+, many people might find themselves in the mire. When I first heard about this tunable transceiver, I thought that it would definitely bring revolutionary change to future metro Ethernet and optical transport networks with its important practical value for flexibly selecting working wavelength. So this article will unveil all of the things about tunable SFP+ optical transceiver.

About 10G DWDM Tunable SFP+
As the demand for great traffic capacity keeps growing, more optical transceivers of different wavelengths are needed. So tunable transceivers are recent innovations in DWDM transport systems. DWDM tunable transceivers are within the scope of DWDM transceivers, through which different DWDM wavelengths can be configured and output in the same optical module. But compare with conventional fixed-wavelength DWDM SFP+, the tunable SFP+ uses tunable laser as light sources in DWDM systems, which is tunable across the entire C-band with 96 channels on the ITU-T 50-GHz grid.

The tunable laser technology is firstly introduced by Oclaro, a leading supplier and and innovator of tunable laser and transceiver solutions. In 2013, it announced a standards-compliant, multi-rate tunable SFP+, which supports rates between 9.95 and 11.3 Gbps. But the first-generation tunable SFP+ optical transceivers were not widely adopted, because they did not meet the critical requirement of less than 1.5 W of power consumption at high operating temperatures. So in 2014, Oclaro demonstrated a new tunable SFP+ module based on a new Oclaro InP tunable laser platform. With the innovative new chip design and the use of next generation materials, the new module is fully compliant to the SFP MSA form factor and can operate at 1.5W at 70 degrees C with excellent OSNR tolerance. With the breakthrough of technology, the 10G tunable SFP+ transceivers become an important component for next generation data center, metro and regional optical network equipment. They meet the world’s growing bandwidth demands while reducing the size and power consumption for 10G connections.
Key Highlights of Tunable SFP+ Module:
(1) Fully compliant with MSA standard size based on SFF-8432 specification for Improved Pluggable Form Factor, rev. 5.1
(2) Tunable across the full C-band with 96 channels on the ITU-T 50GHz grid
(3) Multi-rate operation: 9.95 Gbit/s to 11.3 Gbit/s
(4) Operates at 1.5W at 70 degrees C with excellent OSNR tolerance
Advantages of Tunable SFP+
The tunable SFP+ transceivers are high-performance optics which can be tuned to the appropriate wavelength. The ability to operate on various wavelengths has set these optics apart from fixed-wavelength DWDM SFP+. Besides, These tunable optics will become popular among DWDM systems due to the several advantages.
- Flexible network management
A tunable SFP+ transceiver will be remotely configured for a specific wavelength to support bandwidth changes as needed in Enterprise or Metro networks.
- Reduced network inventory
One tunable SFP+ transceiver will support more than 80 different wavelengths. It will allow network operators to hold one tunable device code as opposed to 80+ fixed wavelength transceivers.
- Reduced power consumption
It will provide a significant reduction in electrical power dissipation compared to other tunable solutions.
- Compact and high-density form factor
The new tunable SFP+ transceiver will be about the size of a pack of gum, saving valuable real estate in data centers.
- Increased network capacity
The tunable SFP+ will double the number of channels supported in this compact transceiver form factor. Upgrading to 50GHz channel spacing doubles the capacity potential in Enterprise and Metro networks.
Conclusion
The advent of 10G DWDM tunable SFP+ transceivers in the market will accelerate the trend for pace-, power-, and cost-efficient network solutions. Because tunability is critical for minimizing inventory and enabling flexible rapid service provisioning. Although now the market share for DWDM tunable SFP+ transceiver is not big enough, the huge potential will be demonstrated in the near future.
 votre commentaire
votre commentaire Suivre le flux RSS des articles
Suivre le flux RSS des articles Suivre le flux RSS des commentaires
Suivre le flux RSS des commentaires


